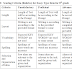
What is Cooperative Learning?
Cooperative or collaborative learning is a team process where members support and rely on each other to achieve an agreed-upon goal. The classroom is an excellent place to develop team-building skills you will need later in life. Cooperative learning is a successful teaching strategy in which small teams, each with students of different levels of ability, use a variety of learning activities to improve their understanding of a subject. Each member of a team is responsible not only for learning what is taught but also for helping teammates learn, thus creating an atmosphere of achievement. Students work through the assignment until all group members successfully understand and complete it. Cooperative / collaborative learning is interactive; as a team member, the student teacher : Develops and shares a common goal Contributes his/her understanding of the problem: questions; insights and solutions Responds to, and works to understand, others' questions, insights and solutions Empowers the other to speak and contribute, and to consider their contributions Is accountable to others, and they are accountable to him/her Is dependent on others, and they depend on him/her .
Elements of Cooperative Learning : The conditions/elements that will ensure more productive than competitive and individualistic efforts are:
1. Positive Interdependence
Each group member's efforts are required and indispensable for group success
Each group member has a unique contribution to make to the joint effort because of his or her resources and/or role and task responsibilities
Cooperative or collaborative learning is a team process where members support and rely on each other to achieve an agreed-upon goal. The classroom is an excellent place to develop team-building skills you will need later in life. Cooperative learning is a successful teaching strategy in which small teams, each with students of different levels of ability, use a variety of learning activities to improve their understanding of a subject. Each member of a team is responsible not only for learning what is taught but also for helping teammates learn, thus creating an atmosphere of achievement. Students work through the assignment until all group members successfully understand and complete it. Cooperative / collaborative learning is interactive; as a team member, the student teacher : Develops and shares a common goal Contributes his/her understanding of the problem: questions; insights and solutions Responds to, and works to understand, others' questions, insights and solutions Empowers the other to speak and contribute, and to consider their contributions Is accountable to others, and they are accountable to him/her Is dependent on others, and they depend on him/her .
Elements of Cooperative Learning : The conditions/elements that will ensure more productive than competitive and individualistic efforts are:
1. Positive Interdependence
Each group member's efforts are required and indispensable for group success
Each group member has a unique contribution to make to the joint effort because of his or her resources and/or role and task responsibilities